We live in a multicultural world, where people of different colours and ethnicities inhabit this “global village” and gradually form a pattern of cross-cultural communication in which encoding and decoding play an important role. Jamaican-British academic Stuart Hall argues that information is encoded by producers in the transmission process, with specific intentions and values, and integrated into different messages. When receiving information, the audience will decode it according to their background and native language, which may be consistent with the original meaning but may also have different understandings.
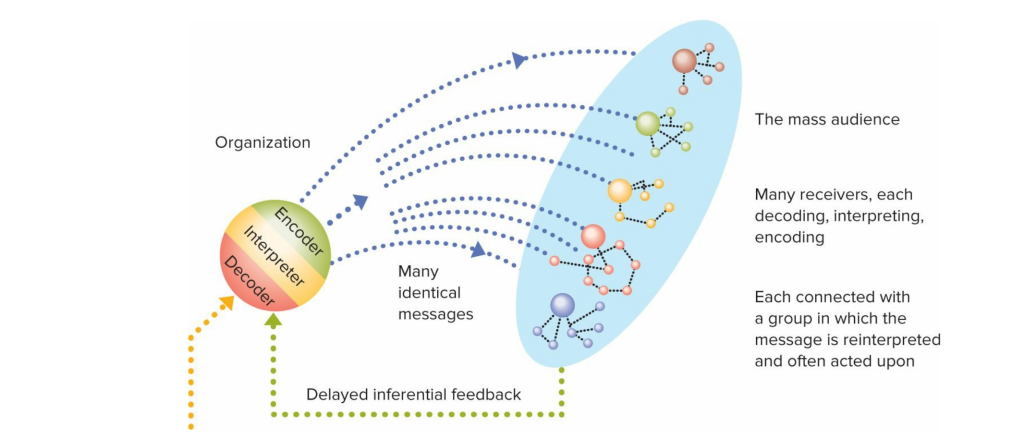
The content of the film hides the patriotic feelings of the In real life, there are many ways to express encoding and decoding well, such as TV series and movies that people often watch. “Wolf Warrior 2” is a patriotic film from China, telling the content of the film that hides the patriotic feelings of the Chinese and their values. The actor “encodes” information such as eye contact, emotional communication, physical contact, and dialogue communication into subtitles. However, if the film is played outside of China, the audience may not be able to understand the original Chinese content, which involves whether the movie subtitles are accurately “decoded” by the subtitle translator. Translators need to deeply understand the content of the film, experience the emotions that the actors need to express, and translate the subtitles, which is “decoding”. I searched the Internet for the opinions of people from different countries about this film, which can well reflect the evaluation of different countries and different cultures.


Australian netizens gave high praise 

These two netizens gave very low scores, 3/10 stars
In Translating Cultures, subtitle translation exemplifies encoding and decoding: the original language content is encoded with the creator’s intent, then decoded and re-encoded by translators to ensure that audiences from different cultures can accurately interpret the cultural meaning (Bassnett & Trivedi, 1999).
In cross-cultural communication, avoiding misunderstandings and cultural biases is especially important. Ideology has a significant influence on translation (Bassnett & Trivedi, 1999). In the process of cross-language and cross-cultural translation, factors such as the translator’s cultural background, depth of education, and understanding of a language will affect the result of the subtitle “decoding”. This recoding of information can affect how audiences interpret it and even their understanding and attitudes towards another culture.
In conclusion, subtitling plays a bridging role in cross-cultural communication, transforming the message, emotion, and intent of the original culture into a form that can be understood by the target cultural audience through the process of encoding and decoding. This transformation is not only linguistic but also involves the transmission of cultural backgrounds and values, thus facilitating a deep level of communication between different cultures.
Reference
Bassnett, S. & Trivedi, H., eds. (1999). Translating Cultures. London: Routledge.
Durham, M.G. & Kellner, D., eds. (2006) Media and Cultural Studies: KeyWorks. Rev. ed. Oxford: Blackwell (KeyWorks in Cultural Studies).
Baran, S.J. (2022) Introduction to Mass Communication: Media Literacy and Culture. 11th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.

